The Supreme Court's Efforts in Combating Gender Stereotyping
Understanding the Initiative:
- In a proactive move, Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud introduces the handbook as a means to challenge outdated and patriarchal notions, particularly when addressing women's issues.
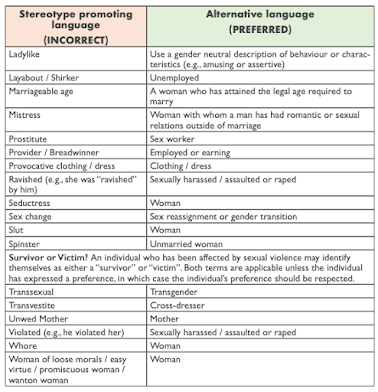
- The handbook provides lawyers and judges with an array of alternative words and phrases to replace gender-unjust terminology in their proceedings.
- It underscores the importance of identifying, understanding, and confronting stereotypes about women.
Transformation in Language:
- The handbook outlines several crucial changes in language usage to eradicate harmful gender stereotypes in judicial decisions and documentation.
- For instance, terms like "adulteress" are replaced with "woman who has engaged in sexual relations outside of marriage."
- The handbook emphasises the removal of preconceived notions such as attaching "chaste" or "obedient" to "woman" and "wife." Instead, the focus is on neutral and unbiased language.
Approach to Addressing Sexual Violence:
- One of the significant highlights of the handbook is its approach to sexual violence cases.
- It advocates using either "survivor" or "victim" to describe individuals affected by sexual violence, acknowledging the complex experiences they go through.
- Stressing the importance of consent, the guidelines emphasise that a woman's clothing should not be linked to questions about her sexual relations.
- The handbook dismisses the notion that delayed reporting indicates falsehood, recognising the courage it takes to report such offences.
Harmful Impacts of Stereotyping:
- The handbook underscores the damaging effects of stereotypes, not only on individuals but also within societal structures.
- It draws attention to how stereotypes lead to exclusion and discrimination in workplaces, educational institutions, and public spaces.
- An example is given how stereotypes about oppressed castes can exacerbate mental pressure on students during exams, affecting their performance.
Empowering Women and Challenging Norms:
- The handbook challenges stereotypes and labels that perpetuate inequalities.
- It asserts that a person's gender does not determine their capacity for rational thought and caregiving abilities.
- This statement underscores the need to dispel traditional notions that have confined women to certain roles.
- The court aims to break down these norms and promote equality.
Incorporating Progressive Verdicts:
The Supreme Court highlights specific verdicts that reject stereotypes and serve as examples for judges.
Adultery Law Struck Down (Joseph Shine vs. Union of India):
- The Supreme Court invalidated adultery law (Section 497 of IPC), citing patriarchal norms and gender biases as its basis.
- The decision challenged societal restrictions on women and aimed to counter unrealistic expectations.
Ban on Two-Finger Test (State of Jharkhand vs. Shailendra Kumar Rai):
- Court banned the invasive "two-finger test" determining rape survivor's sexual history.
- Ruled it irrelevant, protecting dignity and rights, and eliminating victim-blaming.
Credibility of Survivor Testimonies Recognised (State of Punjab vs. Gurmit Singh):
- The court affirmed inherent credibility of rape survivors' testimonies, countering stereotypes and acknowledging reasons for delayed reporting, including social stigma.
Supreme Court's decisions dismantle gender stereotypes, promote equality, and safeguard dignity and rights, especially for women facing historical discrimination and harmful legal practices.
Potential Impact on Society:
- The handbook's release has generated optimism among experts and individuals. Experts views it as a positive step towards altering mindsets.
- The handbook's comparison table (Mentioned above) , Contrasting stereotypes with realities, is seen as a powerful tool in challenging preconceived judgments.
- While change might be slow and gradual, language's transformative power can contribute to a more inclusive legal landscape.
To conclude, The Supreme Court's efforts to combat gender stereotypes through its handbook represent a pivotal move towards equality and justice. By redefining language and challenging societal norms, the court paves the way for a more inclusive legal environment that recognises the dignity and rights of all individuals, irrespective of their gender.
Stereotype Meaning:
- A stereotype is a widely held but oversimplified and generalized belief or idea about a particular group of people, things, or concepts.
- Stereotypes are often based on assumptions, biases, or limited information, and they can lead to unfair and inaccurate judgments about individuals or groups.
- Stereotypes can be harmful as they perpetuate biases, contribute to discrimination, and prevent a deeper understanding of the diversity and complexity within the group being stereotyped.
Click Here to Download : Handbook on Combating Gender Stereotypes






Comments
Post a Comment